Lab 12 - Protecting LLM Provider Token Usage with JWT Authorization
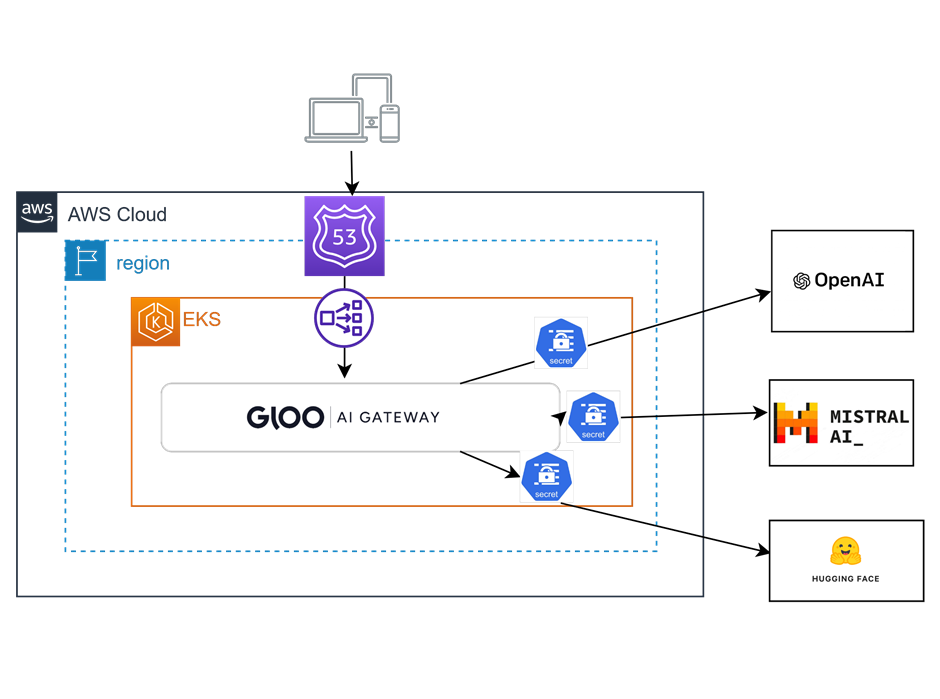
In this lab, JWT tokens will be required from the call initiator to validate the caller’s access to the AI service. Gloo Gateway Virtual Service for Hugging Face AI endpoint will be adjusted accordingly. The setup will be validated using the curl command.
For this workshop, the signing certificate and JWT token are pre-generated and provided here as part of the instructions. You can configure your own artifacts and replace them in the instructions below using tools that are available to you (such as openssl).
-
Assign the token to an environmental variable:
export JWT_TOKEN="eyJhbGciOiJSUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9.ewogICJpc3MiOiAic29sby5pbyIsCiAgIm9yZyI6ICJzb2xvLmlvIiwKICAic3ViIjogInNvbG8td29ya3Nob3AiLAogICJ0ZWFtIjogImRhdGEiLAogICJsbG1zIjogewogICAgImh1Z2dpbmdmYWNlIjogWwogICAgICAiaHVnZ2luZy1mYWNlLWxhdGVzdCIKICAgIF0KICB9Cn0.M8tIhMfgPMAaXdre9aBXuPNYgdtHlyLiK_XvR7GciegogfQDt-Iw0Q9oskphzYLsStPJU8Q2MbYYPznfCtbb-gFhuvckP2wCDP2SvQppov2oGPD9r8uRGrQyRCzaqM9IpAFui5OfzIU1LQStSyNME4Y94Jk6MhGDQjOi62Mvo3G9XmZ1xE_XwAL3FYjiYl0Mwif1D-qoZgBZFjDkr_QC-2eZ_ShmmVHtzq_FP95V3W7MCUAshH-JlWKgQnpXMnNLGKNr_na20R7_8unlIUZNAVmwKadel8pjVv6Ia5juPYahO9hG17kFi3amcF7cz7rdK7_aX1LXQxK94sQ_dgzYaQ"You can examine the token content online using jwt.io, paying attention to the decoded payload:
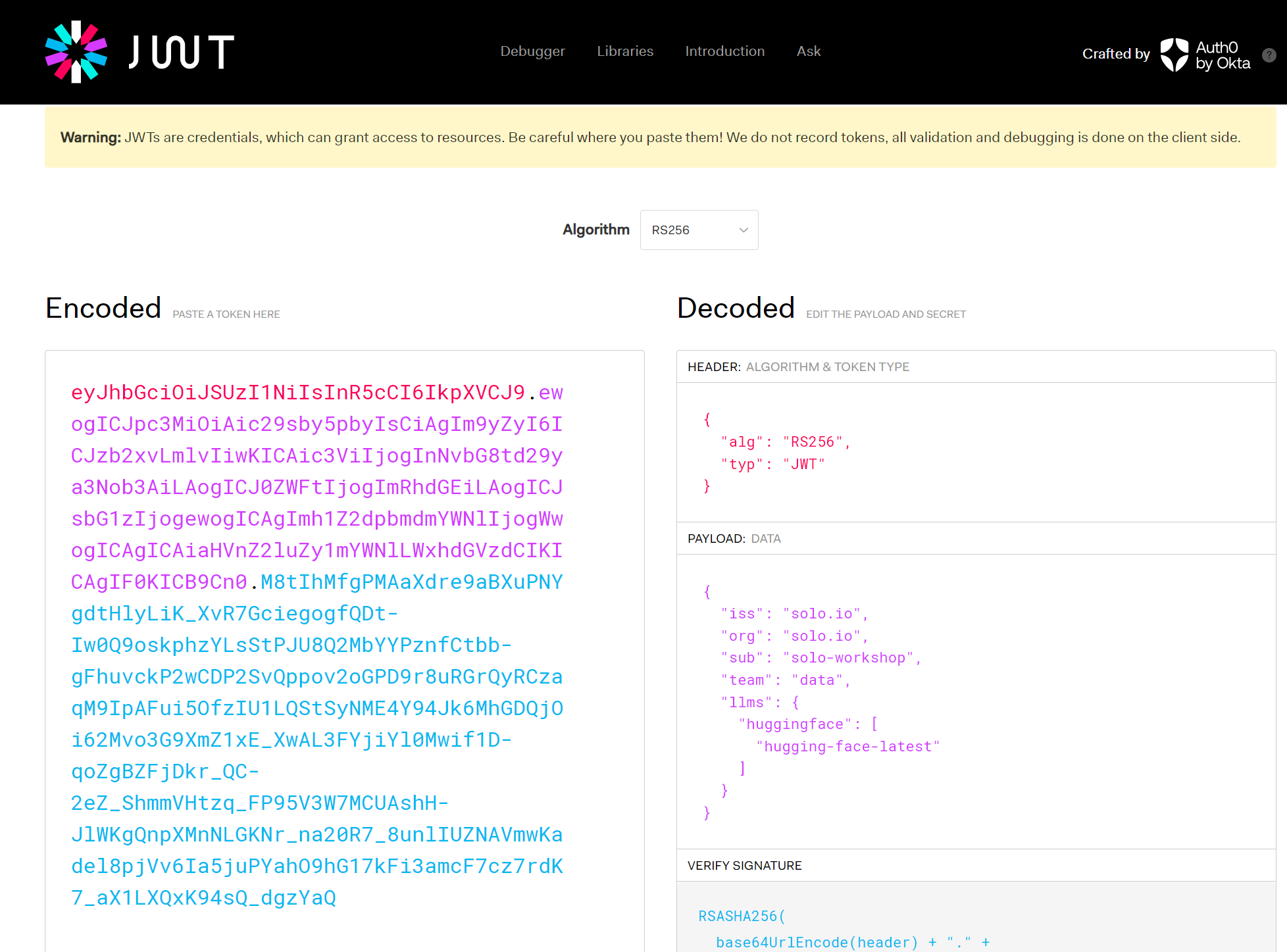
-
Update the Virtual Service with RBAC to allow access only if the required claim details are present and add the public signing certificate for JWT signature validation.
kubectl replace -f - <<EOF apiVersion: gateway.solo.io/v1 kind: VirtualService metadata: name: ai-services-vs namespace: default spec: virtualHost: domains: - "*" options: jwt: providers: selfminted: issuer: solo.io jwks: local: key: | -----BEGIN PUBLIC KEY----- MIIBIjANBgkqhkiG9w0BAQEFAAOCAQ8AMIIBCgKCAQEAskFAGESgB22iOsGk/UgX BXTmMtd8R0vphvZ4RkXySOIra/vsg1UKay6aESBoZzeLX3MbBp5laQenjaYJ3U8P QLCcellbaiyUuE6+obPQVIa9GEJl37GQmZIMQj4y68KHZ4m2WbQVlZVIw/Uw52cw eGtitLMztiTnsve0xtgdUzV0TaynaQrRW7REF+PtLWitnvp9evweOrzHhQiPLcdm fxfxCbEJHa0LRyyYatCZETOeZgkOHlYSU0ziyMhHBqpDH1vzXrM573MQ5MtrKkWR T4ZQKuEe0Acyd2GhRg9ZAxNqs/gbb8bukDPXv4JnFLtWZ/7EooKbUC/QBKhQYAsK bQIDAQAB -----END PUBLIC KEY----- routes: - matchers: - prefix: /huggingface-gloo-gw routeAction: single: upstream: name: huggingface-upstream namespace: default options: autoHostRewrite: true prefixRewrite: "/models/openai-community/gpt2" rbac: policies: viewer: nestedClaimDelimiter: . principals: - jwtPrincipal: claims: llms.huggingface: hugging-face-latest matcher: LIST_CONTAINS headerManipulation: requestHeadersToAdd: - header: key: Content-Type value: application/json append: false - headerSecretRef: name: hftoken namespace: default EOF -
Test the setup:
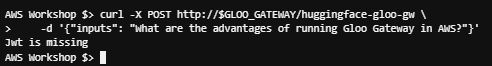
First, run the command from the previous module and confirm the call is not allowed:
curl -X POST http://$GLOO_GATEWAY/huggingface-gloo-gw \ -d '{"inputs": "What are the advantages of running Gloo Gateway in AWS?"}'The request that was successful in the previous lab is now getting blocked as there is no JWT token provided:
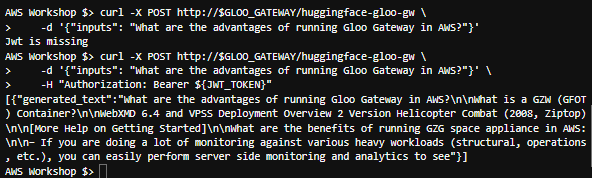
 The command will work as expected after adding the JWT token:
The command will work as expected after adding the JWT token:curl -X POST http://$GLOO_GATEWAY/huggingface-gloo-gw \ -d '{"inputs": "What are the advantages of running Gloo Gateway in AWS?"}' \ -H "Authorization: Bearer ${JWT_TOKEN}"The result should be generated by Hugging Face UI. Since it’s a demo system, the response is not serious, but valid:
In this lab, we introduced control over the usage of the specific service by validating the caller’s permissions by examining the JWT token.