Lab 3 - Routing to other workloads
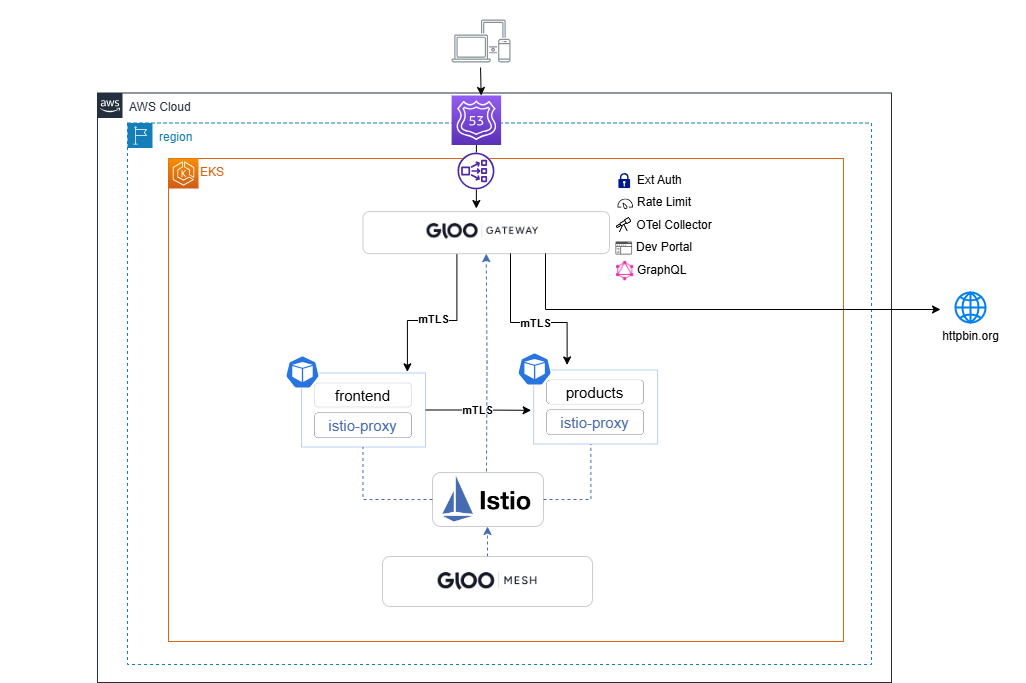
-
Let’s see how easy it is to expose another application. This time, we will match on URI prefix: /products and send to the productcatalogservice application.
kubectl apply -f - <<EOF apiVersion: networking.gloo.solo.io/v2 kind: RouteTable metadata: name: productcatalog namespace: online-boutique spec: weight: 100 workloadSelectors: [] http: - matchers: - uri: exact: /products - uri: prefix: /products name: products labels: route: products forwardTo: destinations: - ref: name: productcatalogservice namespace: online-boutique port: number: 3555 EOF -
Get products from the Product Catalog API.
curl $GLOO_GATEWAY/products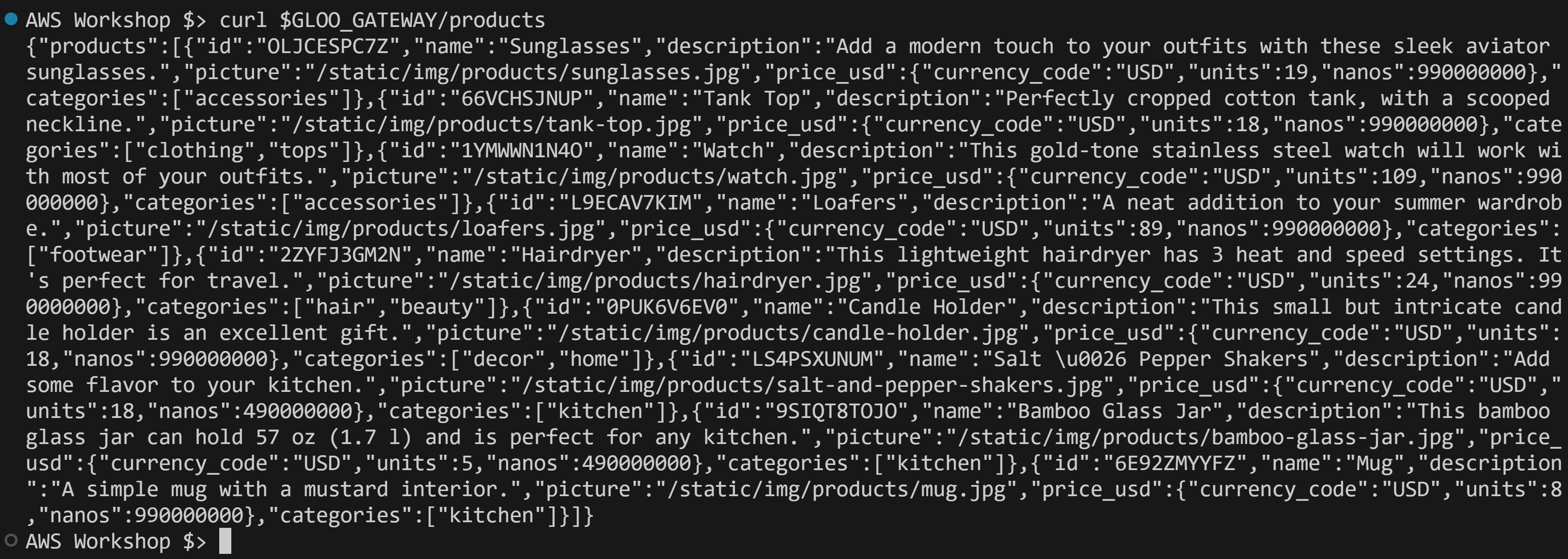
-
Next, let’s route to an endpoint (http://httpbin.org) that is external to the cluster. ExternalService resource defines a service that exists outside of the mesh. ExternalService provides a mechanism to tell Gloo Platform about its existance and how it should be communicated with. Once an ExternalService is created, a RouteTable can be used to send traffic to it. In this example, we will send traffic on URI prefix: /httpbin to this external service.
kubectl apply -f - <<EOF apiVersion: networking.gloo.solo.io/v2 kind: ExternalService metadata: name: httpbin namespace: online-boutique spec: hosts: - httpbin.org ports: - name: https number: 443 protocol: HTTPS clientsideTls: {} ### upgrade outbound call to HTTPS EOF -
Create a new RouteTable that will match on requests containing the prefix /httpbin and route it to the httpbin ExternalService. You may have also noticed that we are rewriting the path using pathRewrite: / because httpbin.org is listening for /get.
kubectl apply -f - <<'EOF' apiVersion: networking.gloo.solo.io/v2 kind: RouteTable metadata: name: httpbin namespace: online-boutique spec: weight: 150 workloadSelectors: [] http: - matchers: - uri: prefix: /httpbin name: httpbin-all labels: route: httpbin forwardTo: pathRewrite: / destinations: - ref: name: httpbin port: number: 443 kind: EXTERNAL_SERVICE EOF -
Let’s test it.
curl -v $GLOO_GATEWAY/httpbin/getThe expected results of the executed commands are illustrated in the screenshot below.
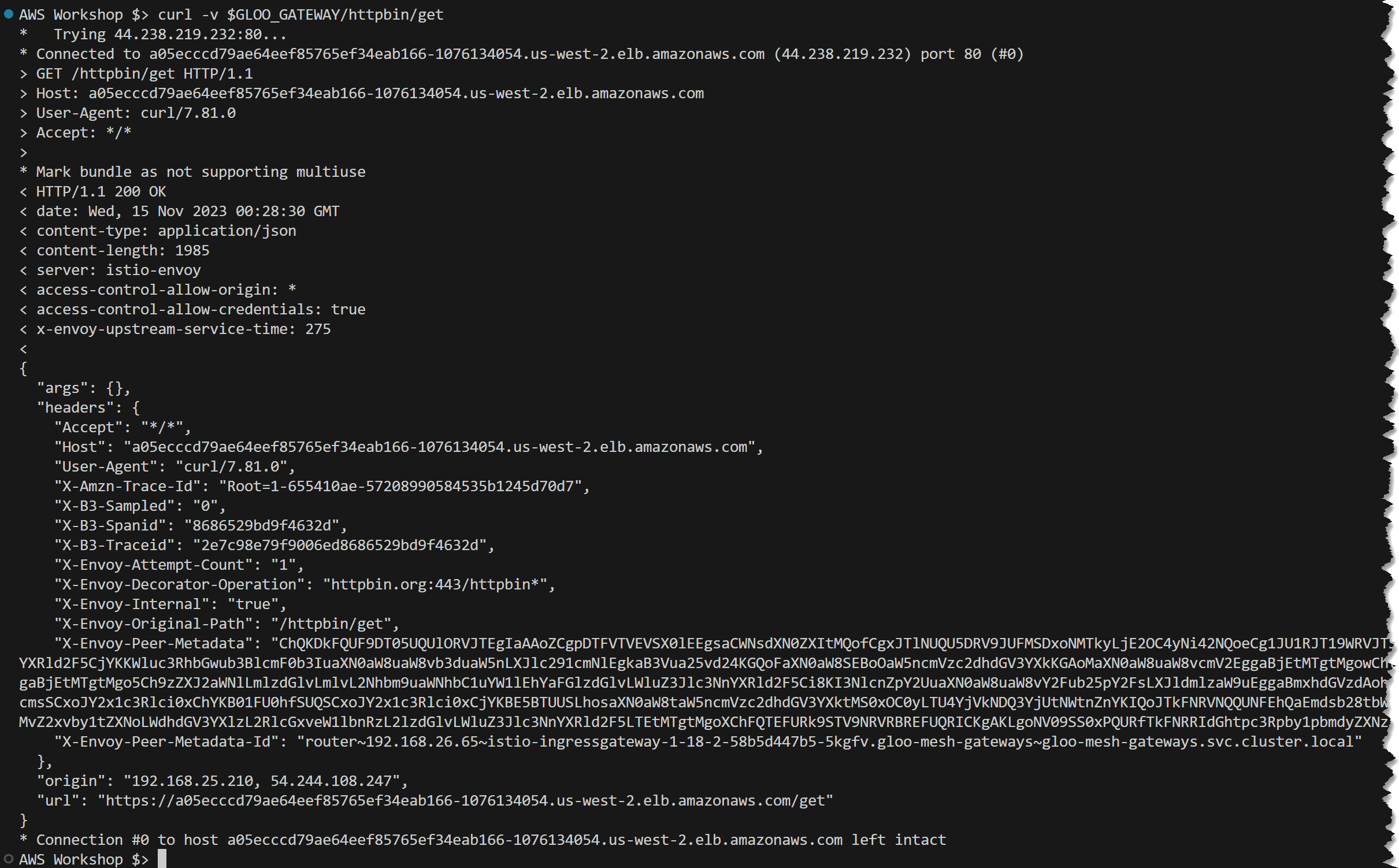
This lab has equipped us with practical knowledge on routing to various workloads, including external services. We’ve successfully exposed another application by matching URI prefixes and routing to services both within and outside our cluster. This lab has demonstrated the flexibility and power of the Gloo Platform in handling diverse routing scenarios, an essential skill in microservices architecture.
As we mastered routing to different workloads, we also gained insights into path rewriting and handling external services, setting a solid foundation for more advanced traffic management.