Lab 11 - Definining Virtual Services for LLM Providers
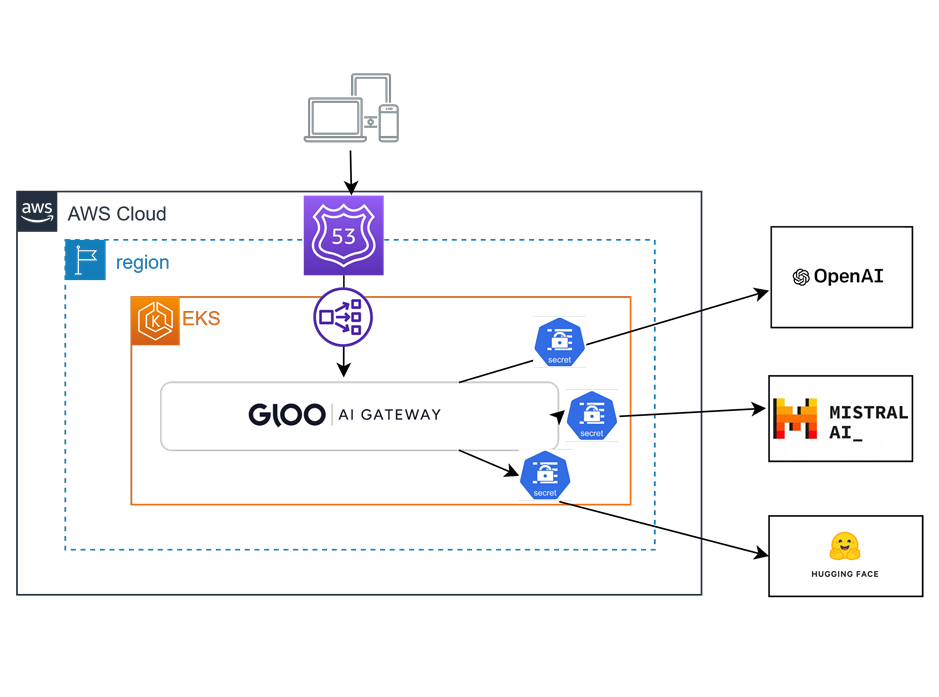
In this lab, a Gloo Gateway Virtual service that contains specifications for Open AI, Mistral and Hugging Face AI endpoints will be created, and a corresponding API Token for Hugging Face will be created as a Gloo Secret. The other services require more complex methods to obtain tokens. If you have access to the tokens yourself, you can implement them similarly to the Hugging Face implementation demonstrated in this lab. The setup will be validated using the curl command.
-
Define the upstream service for Hugging Face APIs:
kubectl apply -f - <<EOF apiVersion: gloo.solo.io/v1 kind: Upstream metadata: labels: app: gloo name: huggingface-upstream namespace: default spec: static: useTls: true autoSniRewrite: true hosts: - addr: api-inference.huggingface.co port: 443 --- apiVersion: gloo.solo.io/v1 kind: Upstream metadata: labels: app: gloo name: openai namespace: default spec: static: useTls: true autoSniRewrite: true hosts: - addr: api.openai.com port: 443 --- apiVersion: gloo.solo.io/v1 kind: Upstream metadata: labels: app: gloo name: mistralai namespace: default spec: static: useTls: true autoSniRewrite: true hosts: - addr: api.mistral.ai port: 443 EOFThe list of upstream defined services can be listed using CLI:
glooctl get upstream -n default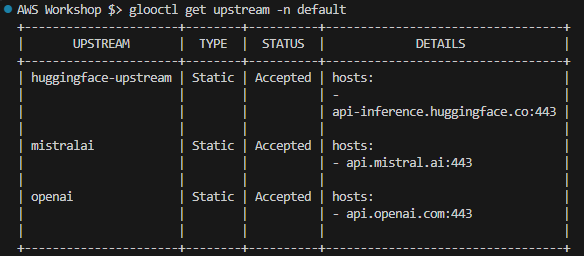
-
Create a secret to store the Hugging Face issued token: You can get it online via the service website free of charge or the instructor will share one with you.
export HF_API_TOKEN=<Hugging Face Token> glooctl create secret header hftoken --headers "Authorization"="Bearer $HF_API_TOKEN" -n default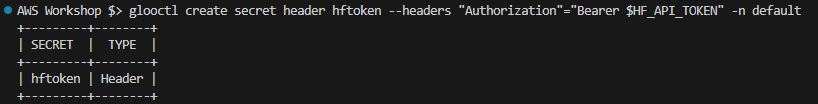
-
Create a Virtual Service that defines listening URI, destination, and adds the token to the request:
kubectl apply -f - <<EOF apiVersion: gateway.solo.io/v1 kind: VirtualService metadata: name: ai-services-vs namespace: default spec: virtualHost: domains: - "*" routes: - matchers: - prefix: /huggingface-gloo-gw routeAction: single: upstream: name: huggingface-upstream namespace: default options: autoHostRewrite: true prefixRewrite: "/models/openai-community/gpt2" headerManipulation: requestHeadersToAdd: - header: key: Content-Type value: application/json append: false - headerSecretRef: name: hftoken namespace: default - matchers: - prefix: /openai routeAction: single: upstream: name: openai namespace: default options: autoHostRewrite: true prefixRewrite: '/v1/chat/completions' headerManipulation: requestHeadersToAdd: - header: key: Content-Type value: application/json append: false - headerSecretRef: name: openai-secret namespace: default - matchers: - prefix: /mistralai routeAction: single: upstream: name: mistralai namespace: default options: autoHostRewrite: true prefixRewrite: '/v1/chat/completions' headerManipulation: requestHeadersToAdd: - header: key: Content-Type value: application/json append: false - header: key: Accept value: application/json append: false - headerSecretRef: name: mistralai-secret namespace: default EOF -
Test the setup:
export GLOO_GATEWAY=$(kubectl -n gloo-system get svc gateway-proxy -o jsonpath='{.status.loadBalancer.ingress[0].*}') curl -X POST http://$GLOO_GATEWAY/huggingface-gloo-gw \ -d '{"inputs": "What are the advantages of running Gloo Gateway in AWS?"}'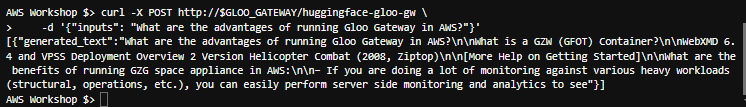
In this lab, we configured Upstream definitions for three different AI public services and created a single Virtual Service that directs customer requests according to the URI path. Since the Hugging Face service token is available to us at no charge, it has been stored as a secret and automatically added to the user request when it traverses Gloo Gateway. In the next lab, we will demonstrate how to limit access to the service based on provided JWT token information.