Lab 4 - AI Integration
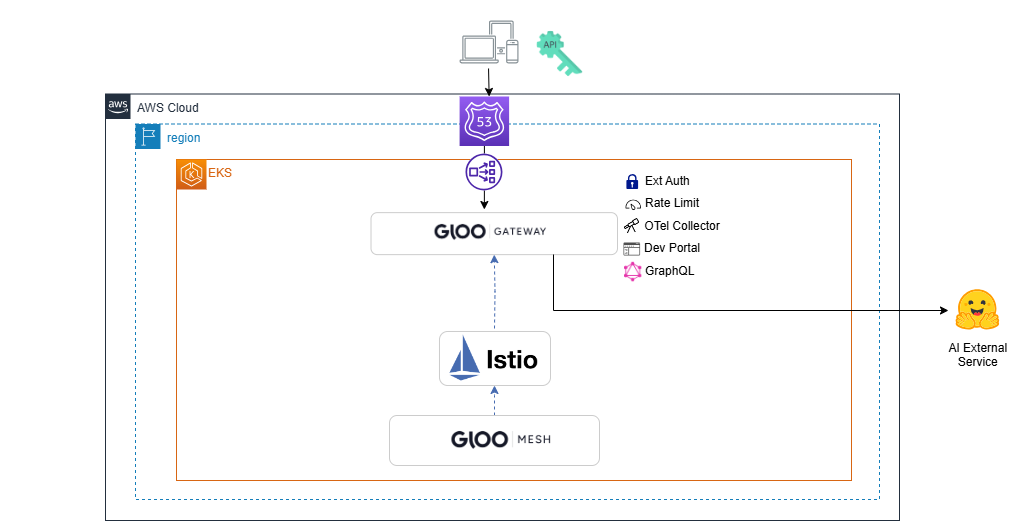
In this lab, we will configure the gateway to forward requests to an AI external service. Technically, any service that responds to HTTP requests can be configured. For the ease of this specific lab, we will use the free Hugging Face service. The requests sent to the lab environment will be intercepted by Istio and forwarded to the external AI service. To complete this lab successfully, you will need to obtain an API Token from your instructor or online.
-
Create ai-demo Namespace to Host AI Related Objects:
kubectl create ns ai-demo -
Enable Port 8081 to the Environment:
- Add port 8081 to the deployed Ingress Gateway. The Gloo Lifecycle Manager (LCM) configures Istio gateways centrally, so the gateway configuration in this step is done by adjusting the LCM configuration. This centralized approach ensures consistent and efficient management of gateway configurations across your environment.:
kubectl patch gatewaylifecyclemanagers.admin.gloo.solo.io istio-ingressgateway -n gloo-mesh --type='json' -p='[{"op": "add", "path": "/spec/installations/0/gatewayRevision", "value": "auto"},{"op": "add", "path": "/spec/installations/0/istioOperatorSpec/components/ingressGateways/0/k8s/service/ports/-", "value": {"name": "http2-8081", "port": 8081, "targetPort": 8081}}]'- Apply Gloo VirtualGateway to handle requests arriving at port 8081 and being processed by AI applications. Also, add RouteTable for all routing to be delegated to RouteTables inside the ai-demo namespace:
kubectl apply -f - <<EOF apiVersion: networking.gloo.solo.io/v2 kind: VirtualGateway metadata: name: ai-ingress-gw namespace: gloo-mesh-gateways spec: workloads: - selector: labels: app: istio-ingressgateway namespace: gloo-mesh-gateways listeners: - http: {} port: number: 8081 allowedRouteTables: - host: '*' selector: namespace: gloo-mesh-gateways --- apiVersion: networking.gloo.solo.io/v2 kind: RouteTable metadata: name: ai-ingress-rt namespace: gloo-mesh-gateways spec: hosts: - '*' virtualGateways: - name: ai-ingress-gw namespace: gloo-mesh-gateways workloadSelectors: [] http: - name: ai-ingress-requests labels: ingress: all delegate: routeTables: - namespace: ai-demo EOF -
Define ExternalService for Hugging Face API Endpoint:
kubectl apply -f - <<EOF apiVersion: networking.gloo.solo.io/v2 kind: ExternalService metadata: name: huggingface-api namespace: ai-demo spec: hosts: - api-inference.huggingface.co ports: - name: https number: 443 protocol: HTTPS clientsideTls: {} EOF -
Create a RouteTable to Rewrite URL and Send Request to the External Service:
kubectl apply -f - <<EOF apiVersion: networking.gloo.solo.io/v2 kind: RouteTable metadata: name: direct-to-huggingface-routetable namespace: ai-demo spec: workloadSelectors: [] http: - name: demo-huggingface labels: route: huggingface matchers: - uri: prefix: /huggingface forwardTo: pathRewrite: /models/openai-community/gpt2 hostRewrite: api-inference.huggingface.co destinations: - kind: EXTERNAL_SERVICE ref: name: huggingface-api port: number: 443 EOF -
Test the Setup:
- Assign the token received from your instructor or issued online to an environmental variable:
export HF_API_TOKEN=<Hugging Face Token>- Assign the Ingress gateway address and port to an environment variable:
export GLOO_AI_GATEWAY=$(kubectl -n gloo-mesh-gateways get svc istio-ingressgateway -o jsonpath='{.status.loadBalancer.ingress[0].*}'):8081 printf "\n\nGloo AI Gateway available at http://$GLOO_AI_GATEWAY\n"- Confirm that the API Token is valid and that the service request sent to the Ingress Gateway managed by Gloo Platform returns a response from the upstream LLM service:
curl http://$GLOO_AI_GATEWAY/huggingface \ -X POST \ -d '{"inputs": "Explain in 1-2 sentences why EKS value significantly increases when Gloo Mesh is added"}' \ -H 'Content-Type: application/json' \ -H "Authorization: Bearer ${HF_API_TOKEN}"The expected results of the executed commands are illustrated in the screenshot below.
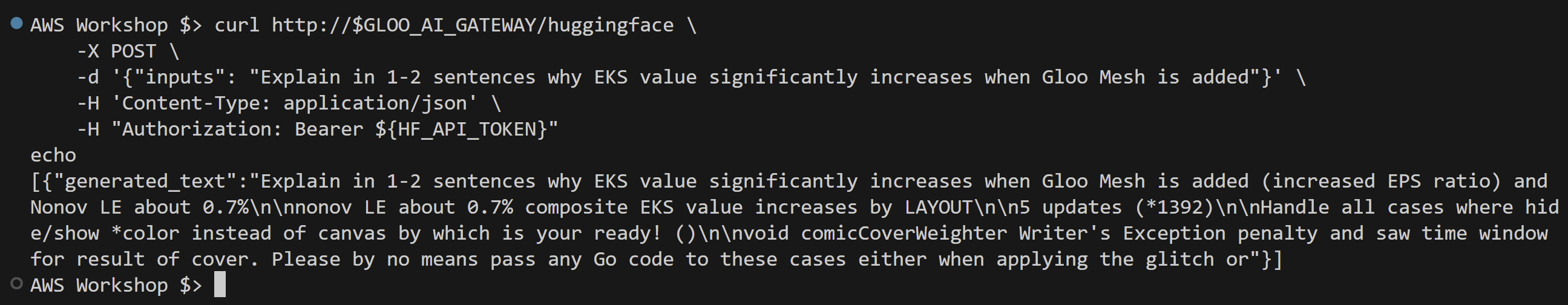
Note: The response in the screenshot is generated using a free model from Hugging Face. While it may provide entertaining and occasionally quirky responses, it’s important to note that for more accurate and meaningful outputs, services like OpenAI’s GPT models are recommended. The configuration process is similar, though OpenAI’s service is not free. Sometimes you get what you pay for - even in AI responses!
This lab has demonstrated the process of integrating AI services with your Gloo Platform on EKS. By configuring external services and routing rules, we’ve enabled the platform to forward requests to the Hugging Face API, allowing seamless AI integration. This capability is vital in modern applications, where leveraging AI services can significantly enhance functionality and user experience. The skills gained in this lab will be instrumental in managing more complex AI integrations and routing scenarios in your microservices architecture.