Lab 8 - Traffic Policies
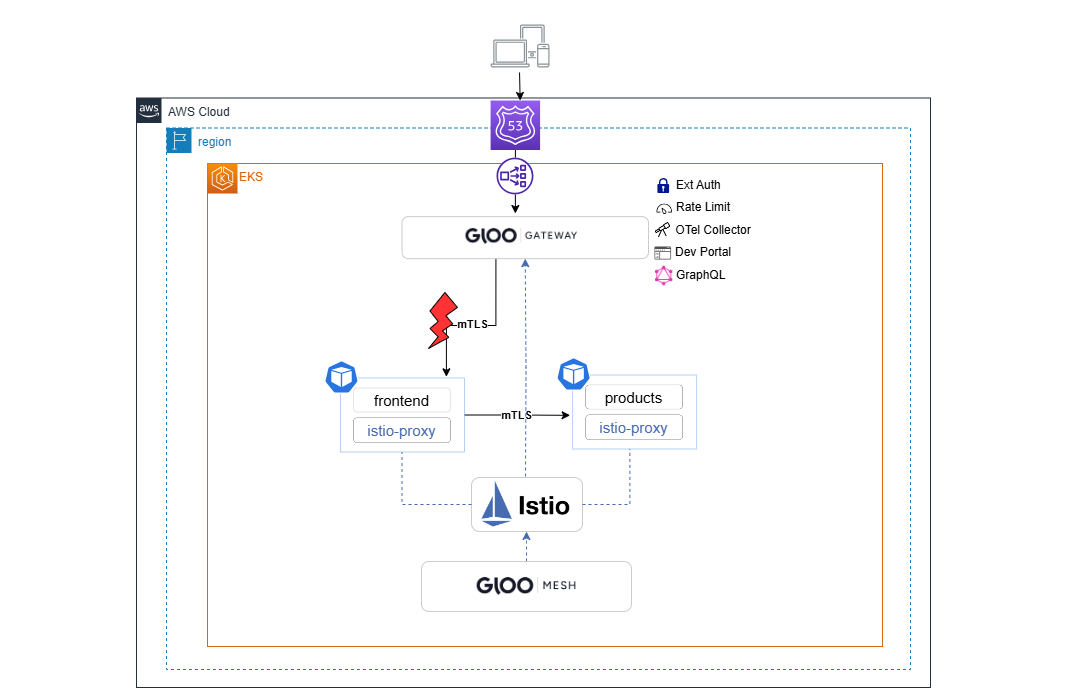
In this lab, we will implement intelligent routing rules for the applications in your cluster using Gloo traffic policies. These policies enable you to optimize responses to incoming requests and apply internal security and compliance standards to individual routes, destinations, or entire workloads. This will help you enforce your networking strategy throughout your microservices architecture.
Gloo Platform supports various policies to ensure network resiliency, traffic control, security, and observability for the microservices in your cluster. These can be applied to both gateway and workloads in the mesh, using Kubernetes labels and selectors that match RouteTables, VirtualDestinations, or workloads.
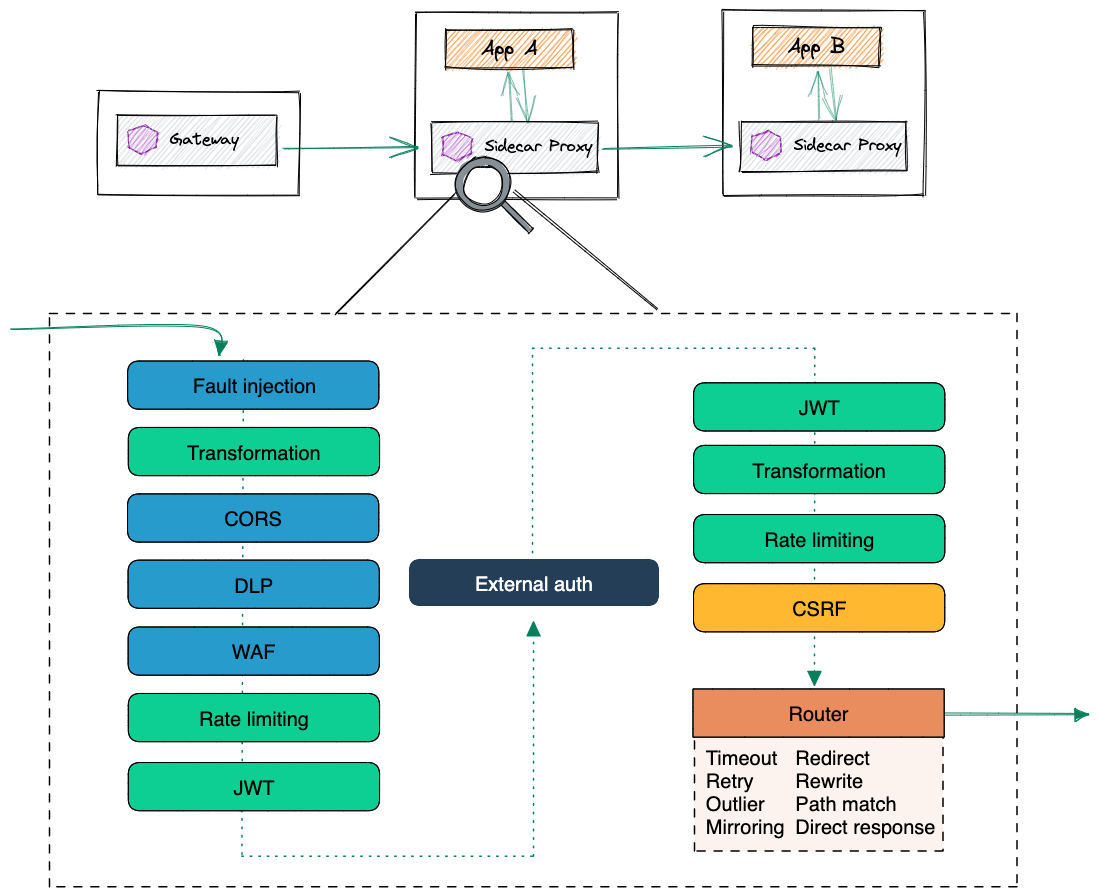
Exercise: Implementing and Measuring Traffic Delay
-
Measure Baseline Response Time: Before applying any traffic policies, it’s important to establish a baseline for the current response time. Use the following curl command to measure this:
curl -o /dev/null -s -w "Time Connect: %{time_connect}s\nTime Start Transfer: %{time_starttransfer}s\nTotal Time: %{time_total}s\n" http://$GLOO_GATEWAY -
Apply a Fault Injection Policy: Now, apply a simple fault injection policy to the frontend RouteTable using its label. This configuration will introduce a 3-second delay:
kubectl apply -f - <<EOF apiVersion: resilience.policy.gloo.solo.io/v2 kind: FaultInjectionPolicy metadata: name: 3sec-fault-injection namespace: online-boutique spec: applyToRoutes: - route: labels: route: frontend config: delay: fixedDelay: 3s percentage: 100 EOF -
Measure the Introduced Delay: After applying the fault injection policy, use the same curl command to measure the response time again. The increase in ‘Time Start Transfer’ and ‘Total Time’ values will demonstrate the delay introduced by the Gloo Platform/Istio service mesh policy:
curl -o /dev/null -s -w "Time Connect: %{time_connect}s\nTime Start Transfer: %{time_starttransfer}s\nTotal Time: %{time_total}s\n" http://$GLOO_GATEWAY
The expected results of the executed commands are illustrated in the screenshot below:
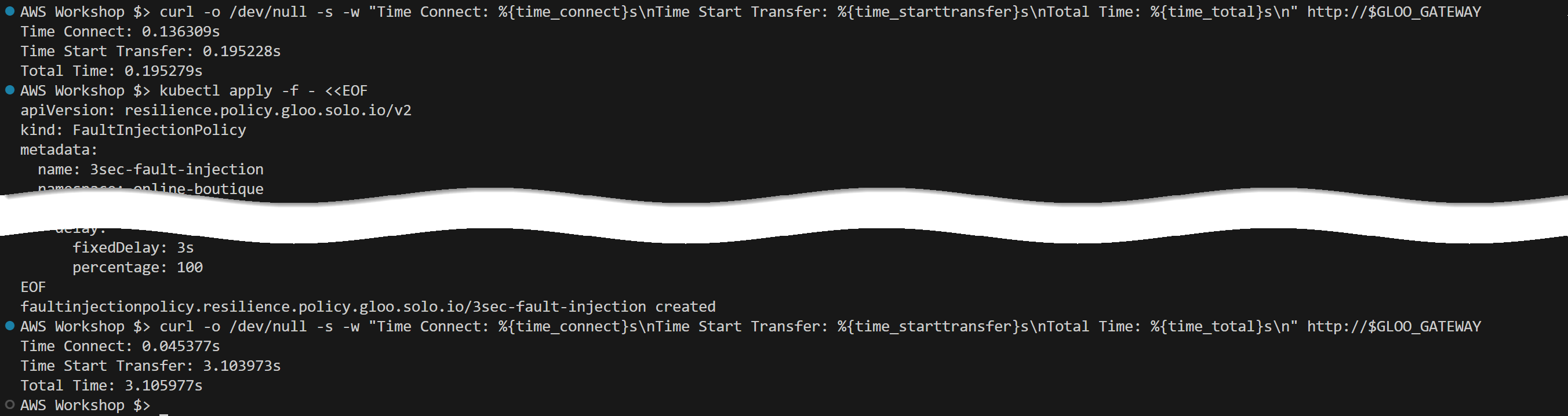
This exercise will help you understand and quantify the impact of traffic policies in a microservices environment.